Picture your small business as a captivating story, each chapter representing a growth stage.
In this article, we'll answer what the five stages of small business growth are, and equip you with the tools and strategies you need to plan and execute each one.
Like a captivating narrative, your business will unfold with its unique challenges and successes.
Planning carefully for each chapter can shape your business's storyline and ensure it captivates your audience—the customers.

The Importance of Small Business Growth
1. Economic development & job creation
Small businesses contribute significantly to employment opportunities, and as these businesses grow, they expand their workforce and stimulate economic activity while reducing unemployment rates.
2. Innovation & competition
Business expansion typically means investment in research and development, creating new products, services, and processes, enhancing customer experiences, and promoting healthy competition.
What Are the 5 Stages of Small Business Growth?
The five stages of small business growth are existence, survival, success, takeoff, and maturity. These are identified by Neil C. Churchill and Virginia L. Lewis in their book of the same name.
In this article:
Let’s look at how to plan effectively for these five stages of business growth.
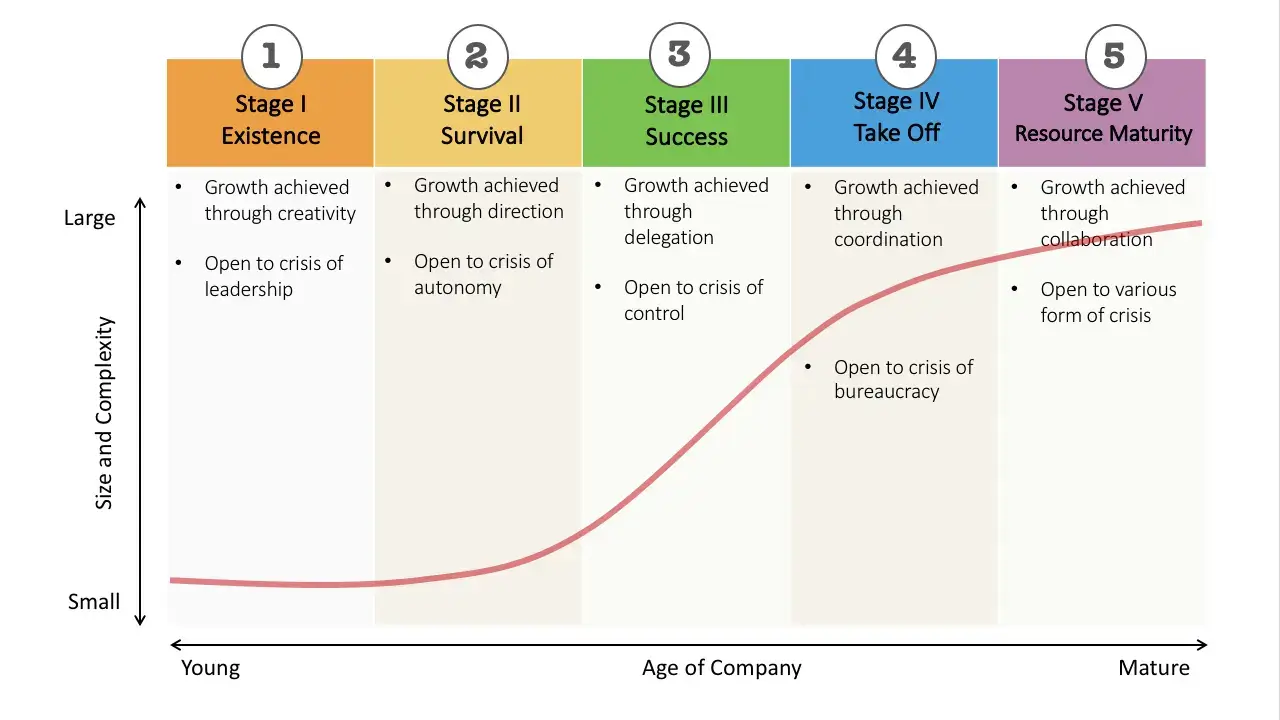
1. Existence
Existence is the initial stage of a small business, focusing on establishing a market presence. The key challenges and objectives during this first stage are:
- Developing a viable product or service: Creating products or services that will meet customer needs and offer value in the market.
- Acquiring customers: The first customers are crucial for establishing a customer base and generating early revenue.
- Managing cash flow: Vital to cover rent, inventory, salaries, and marketing costs.
- Implementing effective marketing strategies: A professional website with an attractive design and user-friendly interface will attract customers. Consider registering a domain name with a relevant extension, such as .ai domain, for businesses in the artificial intelligence industry to enhance brand identity and online presence.
Growth strategies for planning and managing the existence stage to move towards a stable company include:
- Conducting market research: Understand the target market, customer needs, and competitors to develop a product or service that stands out.
- Creating a solid business plan: Define the business's vision, mission, target market, marketing strategies, and financial projections. Using an AI business plan generator that can help you create a comprehensive business plan, guiding you through defining your business's vision, mission, target market, marketing strategies, and financial projections with ease.
- Building a network: Establish connections with potential customers, industry peers, and mentors who can provide guidance and support.
- Managing resources wisely: Start lean by minimizing costs and using available resources efficiently, leveraging tools such as financial reporting and consolidation software to streamline and enhance financial management. Prioritize essential expenses and explore cost-effective marketing channels.
- Monitoring and managing cash flow: Keep a close eye on income and expenses, maintain accurate financial records, and explore potential financing options like a government-backed loan. Consider seeking professional financial advice.
According to Andrew French, Business analyst at Simpalm,
"Successfully navigating the existence stage sets the foundation for the business to move forward into the subsequent growth stages."
2. Survival
A business has demonstrated its viability and generates enough revenue to cover its costs and sustain itself. Predicting sales with a CRM system, such as Clari software, involves using smart technology to look at past sales data and current market trends.
This stage of business growth includes these key challenges and objectives:
- Maintaining financial stability: Ensuring your revenue is sufficient to cover expenses, including salaries, rent, inventory, and other operational costs.
- Operational efficiency: Streamlining processes, improving productivity with productivity tips, and reducing costs without compromising the quality of products or services.
- Customer retention: Retaining existing customers by delivering excellent customer service, building strong relationships, and addressing their evolving needs.
- Competition: Find ways to differentiate the offered products or services to keep up with competitors.
- Scalability: Evaluate the business model and identify opportunities to scale operations while effectively managing resources.

To successfully plan and manage the survival stage, consider the following:
- Continuously monitoring and managing cash flow: Develop a robust financial management system, track income and expenses regularly, and create cash flow forecasts. Explore ways to improve cash flow—such as offering discounts for early payments.
- Focusing on customer satisfaction and retention: Provide exceptional customer service, personalize interactions, and seek feedback to understand customer preferences and address their needs effectively. Implement schemes like loyalty programs to encourage customer loyalty.
- Streamlining operations and reducing costs: Identify areas of inefficiency or wastage and establish methods to optimize processes, reduce expenses, and increase productivity. Consider technology solutions that can automate tasks.
- Managing internal control deficiencies: Regularly assess and address the effectiveness of internal control deficiencies. It includes implementing segregation of duties, establishing transparent approval processes, and conducting regular audits to ensure financial integrity.
- Building strategic partnerships: Collaborate with complementary businesses or form alliances to help expand the customer base or improve operational efficiency.
- Setting realistic goals and milestones: Establish clear objectives and key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress. Regularly review and adjust strategies based on market conditions and business performance.
3. Success
The success stage represents a significant milestone for a small business where it has established a strong market presence and achieved consistent growth.
You should feel confident you have a thriving small business at this stage. But don’t get complacent! The key challenges and objectives during this stage include:
- Scaling operations: Effectively manage the growth of the business by expanding production capacity, improving distribution channels, and enhancing infrastructure to meet the increasing demand.
- Establishing market dominance: Maintain a competitive advantage by continuing to differentiate the products or services, thus securing a larger market share.
- Ensuring sustained profitability: Optimize pricing strategies, manage costs, and improve overall financial performance.
- Deepening customer relationships: Focus on enhancing loyalty and identifying opportunities for upselling or cross-selling.
- Attracting and retaining top talent: Support the business's growth by adding skilled employees, managers, and executives who can contribute to the company's success.
- Building brand awareness: Invest in marketing strategies such as targeted campaigns to reach new customer segments and expand the business's reach.
- Enhancing Business Performance through Innovative Growth Strategies: Implementing Small Business Growth Hacks helps businesses drive continued success by adopting creative strategies that give them a competitive edge and keep them ahead of the competition, such as leveraging social media marketing tactics, optimizing conversion rates through website optimization, implementing referral programs to incentivize customer referrals, and utilizing data-driven insights to make informed business decisions.
4. Takeoff
In the Takeoff stage, the business undergoes rapid growth and expansion. To meet the growing demand, it typically requires increased resources—such as financing, personnel, and infrastructure.
Focus on the key challenges and goals during the stage, including:
- Managing rapid growth: Challenges associated with scaling operations include increased demand, production capacity, and distribution capabilities while maintaining quality standards.
- Accessing additional resources: Secure additional financing, resources, and talent to support the business's expansion plans and meet the market's growing demands.
- Market penetration and customer acquisition: Develop strategies to penetrate new markets, expand the customer base, and reach a wider audience while maintaining strong relationships with existing customers.
- Capturing wholesale eCommerce value: Tap into new customer segments, increase sales volume, and streamline the wholesale ordering process. Leverage the power of digital platforms, such as AI-powered online stores, to attract wholesale customers and offer them a seamless and efficient purchasing experience.
Strategies for planning and managing the takeoff stage include:
- Developing a growth plan: Create a comprehensive strategy that outlines specific objectives, target markets, and expansion plans.
- Strengthening operational efficiency: Optimize internal processes, implement automation and technology solutions, and establish performance metrics to ensure smooth operations.
- Securing additional financing: Explore funding options such as business loans, equity investment, and government grants or rely on startup funding consultants to access the necessary capital for expansion and infrastructure development.
- Expanding marketing efforts: Invest in targeted marketing campaigns, digital marketing strategies, and sales expansion initiatives to reach new markets, acquire customers, and build brand awareness.
- Monitoring and adapting strategies: Continuously monitor key performance indicators, market trends, and customer feedback to assess the effectiveness of growth strategies.
5. Maturity
A plateau in growth characterizes the fifth stage of Maturity.
The business reaches its full potential in size and market share, and its focus shifts towards maintaining profitability and market dominance. Focus on the key challenges and goals during the stage, including:
- Maintaining competitive advantage: As the business matures, it faces the challenge of sustaining its competitive edge in the market. It must continue to differentiate itself from competitors.
- Managing scalability: The business may face challenges when scaling operations or expanding into new markets. Managing growth without compromising quality or customer satisfaction is crucial.
- Adapting to market changes: The business must remain agile, including changing customer preferences, technological advancements, and industry regulations.
- Identifying new growth opportunities: To sustain long-term success, the business must proactively identify and capitalize on new growth opportunities. It may involve exploring new markets, diversifying product/service offerings, or pursuing strategic partnerships and acquisitions.

Planning for the final small business growth stage includes:
- Fostering continuous innovation: Identify new opportunities, improve existing processes, and stay competitive.
- Maintaining strong customer relationships: Implement personalized experiences, exceptional customer service, and loyalty programs for solid customer relationship management. Continuously seek feedback to improve customer satisfaction.
- Exploring strategic diversification: New markets, customer segments, or product/service offerings that align with the business's core competencies and present growth potential.
- Continuously monitoring market trends: Identify in-depth customer preferences and industry dynamics to adapt strategies, identify emerging opportunities, and mitigate potential risks.
- Optimizing financial performance: Maintain effective cost management, efficient budgeting, and proactive cash flow management. Leveraging advanced FP&A software can streamline these processes, offering real-time insights and data-driven decision-making capabilities. Regularly review and adjust financial strategies to align with business goals and market conditions.
Plan for Success with The Five Stages of Small Business Growth
Each of the five stages of small business growth has unique challenges, objectives, and strategies for growth.
Throughout the stages of growth, decision-making processes become more formalized, and strategic planning plays a crucial role in managing growth for the thriving small business effectively.
Understanding the stages can help small business owners anticipate and plan for each phase's specific needs and opportunities, from choosing domain names to strategic diversification, ultimately leading to sustained success and profitability.


