The nature of businesses has become diverse with time. Even the advent of retailers has made supply-demand chains more complicated yet profitable.
Today, companies do not follow business to customer (B2C) model only; instead, they are offering products and services beyond borders and opting for Business-to-Business (B2B) and Business-to-Business-to-Customer (B2B2C) models.
Selling software as a service (SaaS) differs from selling products in the real world. SaaS products are not tangible, so the first challenge is to quantify SaaS products, then decide on their units and make invoices based on these units. And any mistake in this process can ruin your customer relations.
Let's delve into the details of the subscription business model.
What Is The Subscription Business Model?
The subscription business model for SAP uses the recurrent need to identify the ideal customer, and the SaaS product or services are sold recurrently to the same customer base after intervals.
This business model is so famous among SaaS vendors like SAP because of the following advantages:
- The customer is satisfied because they pay only for what they use
- The retailer’s revenue streams are maintained with recurrent billing
- Revenue remains predictable for retailers
- Convenient for customers to pay affordable rates
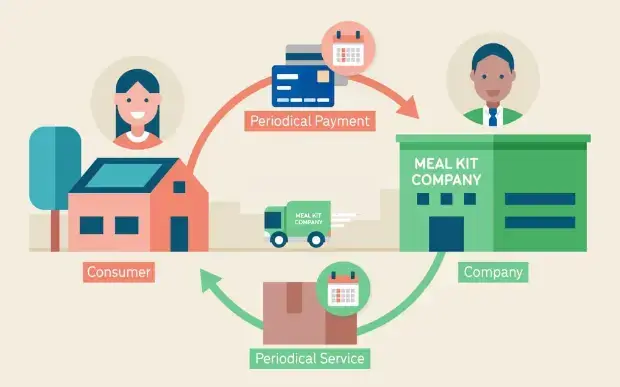
There are many more benefits of the subscription billing model that offer a win-win situation for both SaaS retailers and the customer.
Different Pricing Models For Subscription Businesses
- Flat fee billing
- Usage-based billing
- Pay-per-use billing
- Hybrid billing
With time, the subscription business model became famous because, in this business model, there is the option to choose the pricing model that fits your business needs. And these pricing models consider the following:
1. Flat fee billing
In the flat fee billing model, SaaS subscription businesses set a fixed price for your SaaS product, and subscribers opting for this subscription pricing model pay a fixed subscription rate after the subscription lifetime ends.

2. Usage-based billing
The usage-based pricing plan enables retailers to charge customers based on their usage. For instance, customers opt for postpaid for their mobile phone usage and pay bills to their telecom companies for what exactly they use.
3. Pay-per-use billing
The SaaS product is divided into units in the pay-per-use billing model, and the customer is charged only for the units used. For instance, in some countries, people pay for units of electricity that they use.
4. Hybrid billing
A hybrid billing model allows retailers to opt for different pricing models and mix them in a way that will benefit their business. Also, it is the most widely used pricing model by subscription businesses.
For B2B Business, the subscription billing model is the best because it will allow you to bill customers in a way it benefits you and your customers.
Convenience & Flexibility
Software and business solutions (especially the ones hosted on the cloud) are sold on the subscription business model and are flexible and scalable. They can integrate with other applications and software with time.

Businesses grow with time, and as they grow, their business needs increase. These needs can be fulfilled with more automated software and applications.
SAP offers software and applications such as a SAP composable storefront that integrate with third-party applications and platforms to facilitate customers seamlessly running their businesses.
Is The Subscription Billing Model The Future?
Now that the basics of the subscription billing model are straightforward, it is time to address how the subscription billing model is the future (especially for SaaS).
The businesses opting for the subscription billing model are ready to embrace a bright future because this model has its foundations in predictive analysis.
Businesses can track their performance by monitoring these Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):

These indicators are monitored based on in-depth customer data analysis. And then, predictions are made based on the customer data. SaaS retailers are prepared for the future because they have data.
If you are also a SaaS vendor, embrace the subscription billing model, which fits all your business needs, and implement it with the help of subscription management software.
Even the businesses that we could never think run on this business model have found the recurrent needs of their customers and are successfully flourishing and heading to the future.
Conclusion
Adopting the subscription business model has positioned itself as a pioneer of the future market, particularly for SaaS merchants such as SAP.
This approach presents various benefits, such as the assurance of steady revenue streams, added convenience for consumers, and a range of customized pricing options to match individual business needs.
Moreover, the subscription model exhibits high flexibility, scalability, and seamless integration with diverse software and applications.
Besides, companies can effectively track their performance metrics using key performance indicators (KPIs) and predictive analysis, which assist them in adequately preparing for upcoming challenges.
SaaS vendors must wholeheartedly embrace the subscription billing model to ensure their businesses thrive and expand.

