Did you know that 52% of customers take their business elsewhere if you fail to provide them with personalized experiences?
Having a sharp intuition is something that makes you stand out from the crowd when running a business.
However, you can’t always rely on your gut or instinct to make decisions, as things don’t always go as you expect them to.
Leveraging data is your best bet to make informed decisions and offer tailored experiences to your customers.
Article Shortcuts:
- What is Qualitative Data?
- What is Quantitative Data?
- Difference Between Qualitative and Quantitative Data
- FAQs
You may consider qualitative or quantitative data and sometimes a mix of both. However, to analyze your data and deduce useful findings, it’s best that you know what distinguishes the two data types.
Understanding the nature of the data accessible to you enables you to choose fitting analysis methods and techniques.
As a result, it becomes easier for you to deduce the findings and extract meaningful insights from the data. In this article, we will help you understand the key differences between qualitative and quantitative data.
So, without further ado, let’s begin.

What is Qualitative Data?
Qualitative data encompasses insights or information that you infer descriptively. You can’t use scales or numbers to collect or measure it.
The qualitative data allows you to dive deep when finding answers to your questions. The insights you access when collecting qualitative data are elaborate, facilitating complex decision-making processes.
The qualitative data caters to questions like “why” and “how.” It helps you look beyond the zeros and ones.
For example, when you want to know what makes your customers tick and makes them prefer your brand over other alternatives in the industry, the use of qualitative data may be a viable approach.
Qualitative data may also come in handy when asking your customers for their feedback to improve the solutions you offer.
The feedback from your customers fuels your growth. Therefore, you may need to consider leveraging qualitative data to expand your operations.
You may also need qualitative data to study the behavior of your target audience and explore the reasons behind the decisions they make. To gather such data, you can conduct user research on your target audience with the help of user interview tools.

Source: LocaliQ
Qualitative data encompasses subjective assessment as you explore the causes of the problem, different behaviors, and perceptions of the intended audience.
What is Quantitative Data?
Quantitative data encompasses information that you can gather, analyze, and store in numbers. It caters to the questions like “how much” and “how many” compared to “why” or “how.”
For example, the use of quantitative data is viable when you choose to track your website traffic or monitor the performance of traffic sources.
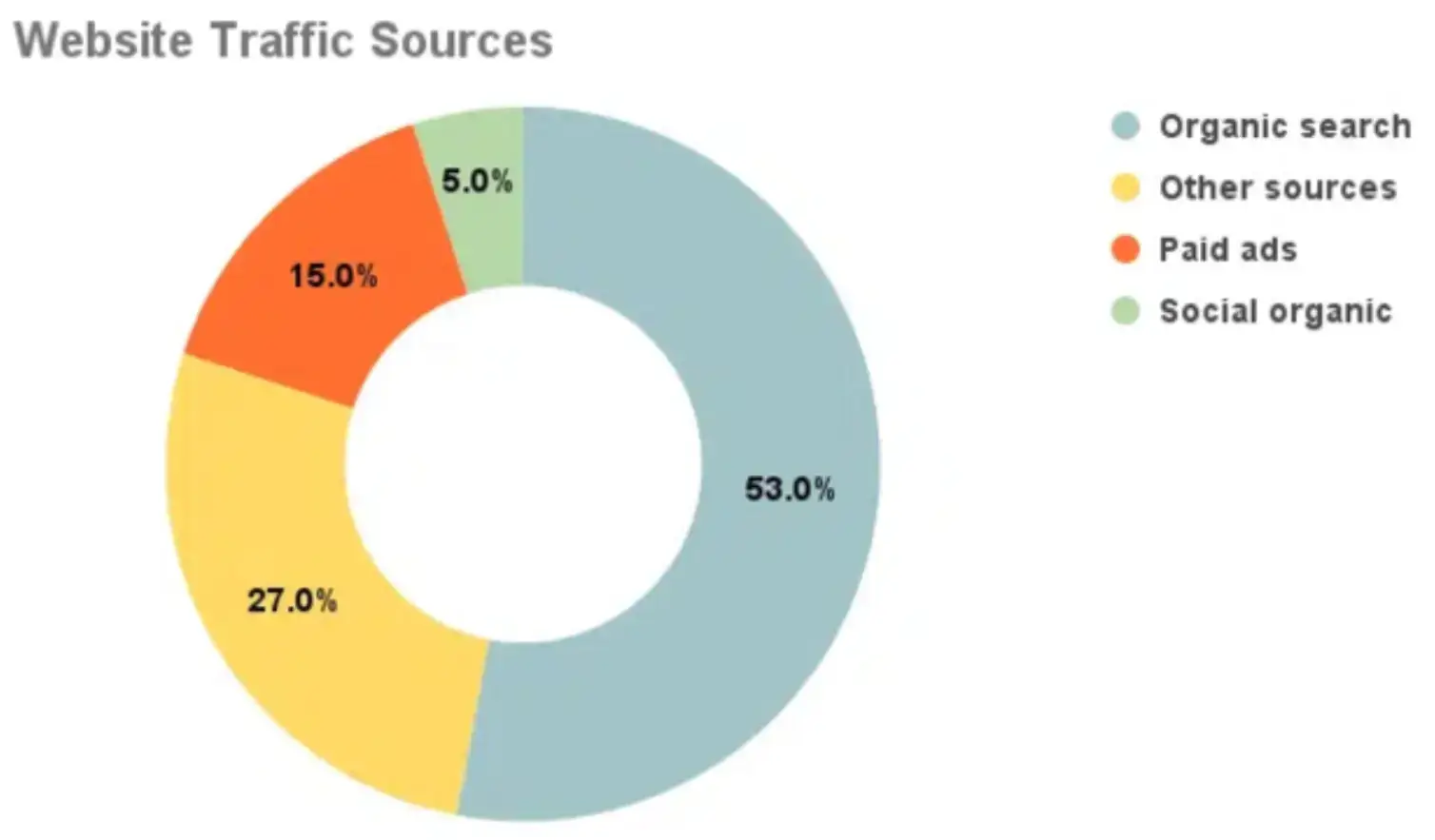
Source: Monster Insights
Quantitative data also comes into play when you want to track other key performance indicators representing your efficiency or the growth of your business.
You extract valuable insights from quantitative data through values and counts. It helps you measure or assess things rather than describe them.
With quantitative data, you can back your decisions with numbers. You use tables, charts, and diagrams to present your findings or insights with ease.
Difference Between Qualitative and Quantitative Data
Leveraging data to fuel your decisions is a smart tactic. However, to make the most of the data at your disposal, you must understand what you’re dealing with.
How you analyze the data and interpret the findings may vary depending on the type of data accessible to you.
You must know how to distinguish qualitative data from quantitative. The following are a few key differences that may help:
1. The Nature
You can distinguish between qualitative and quantitative data by looking at the problem that a particular dataset helps you solve.
The essence of quantitative data is objective. It deals with quantifiable indicators and helps you measure things.
For example, you may consider leveraging quantitative data when you want to know the increase in visitors to your website compared to the previous week.
On the other hand, the nature of qualitative data is subjective. It helps you uncover the details concerning the problem for which you wish to seek solutions.
For example, qualitative data may be suitable to explore the types of content that give you the best results.
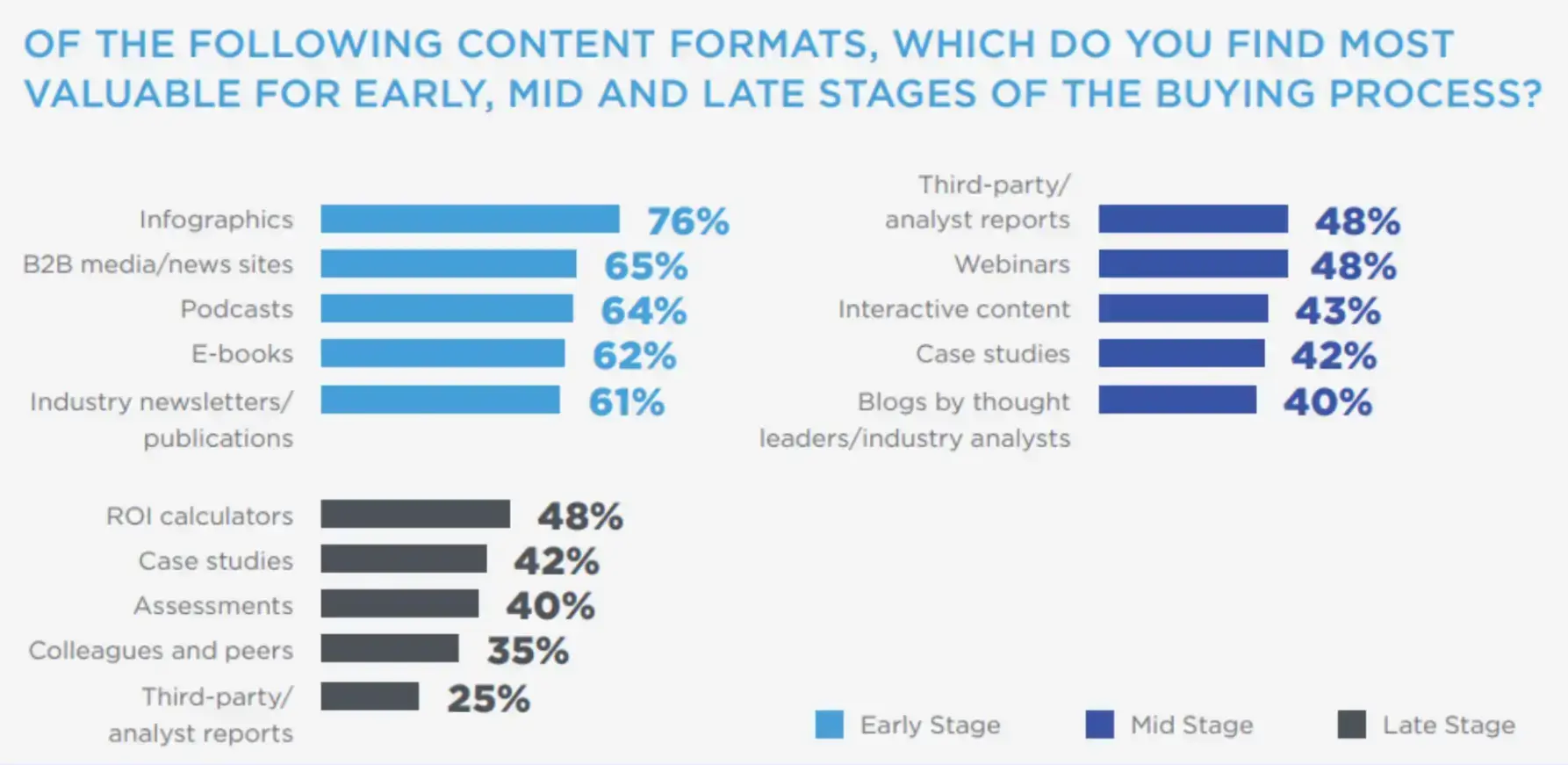
Source: E2M
2. Methodology
Qualitative research encompasses exploratory research methodology. It facilitates your access to information that fuels your understanding of a particular matter and provides you with useful insights.
The research methodology representing quantitative data is conclusive. It facilitates your access to information that can help you test your hypotheses and deduce measurable findings.
An exploratory research methodology enables you to assess behavioral patterns and collect useful customer data showcasing their experiences.
A conclusive research methodology helps you make predictions and sound decisions based on quantifiable data.
3. Sampling
The sampling techniques and the sample size encompassing quantitative and qualitative data are different.
You often require a large sample when conducting quantitative research. However, qualitative research doesn’t need a huge sample size.
The commonly used sampling techniques for quantitative research are simple random sampling, cluster sampling, stratified sampling, systematic sampling, and so on.
The sampling techniques frequently used for qualitative research are purposive sampling, convenience sampling, snowball sampling, quota sampling, etc.
4. Data Collection
Your choice of data collection methods may vary based on the type of data you want to collect for your research.
If you choose to collect quantitative data, the data collection methods you may want to consider are surveys and polls.
On the other hand, the fitting collection methods for qualitative data can be interviews, focus groups, observations, case studies, and so on.
The way through which you gather information for analysis points out another key difference between qualitative and quantitative data.
5. Analysis Technique
You can differentiate qualitative and quantitative data based on your choice of analysis techniques when extracting valuable findings from the datasets.
When analyzing quantitative data, you can choose to go with a variety of descriptive and inferential statistical techniques.
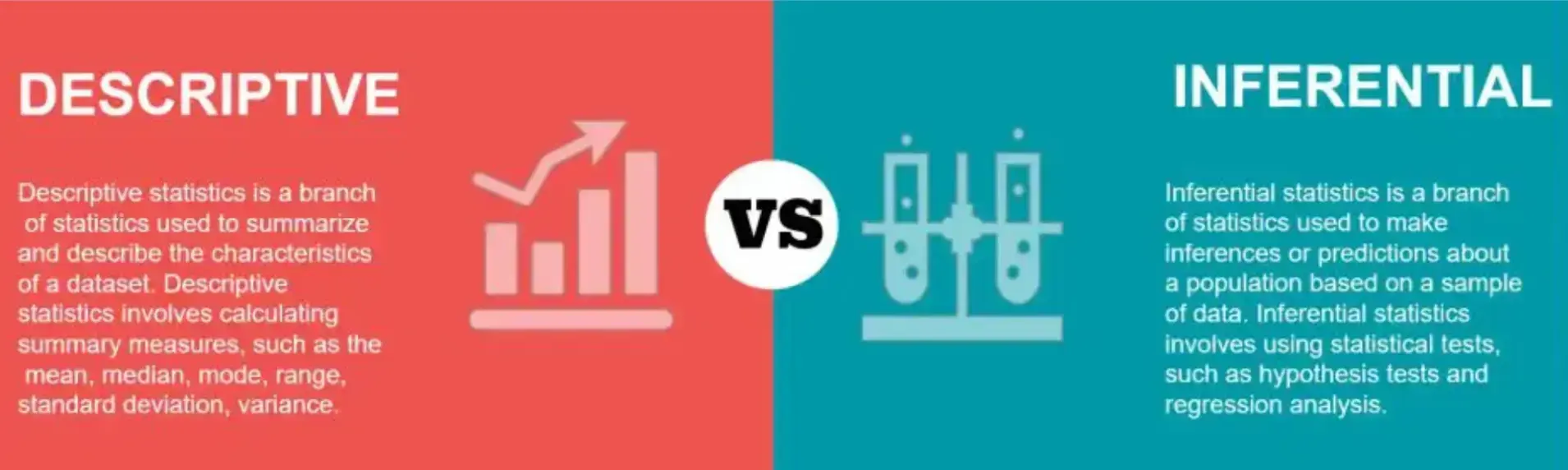

Source: QG
To extract useful findings from qualitative data, the techniques that you may want to consider are narrative analysis, thematic analysis, grounded theory analysis, and discourse analysis.
Quantitative data requires number crunching to access valuable insights. On the other hand, qualitative data requires you to create themes and scenarios to extract useful findings.
FAQs
1. Is there any other research type than qualitative and quantitative?
Yes! There’s one other research type that is not qualitative or quantitative. Actually, it’s an amalgamation of both research methods. It’s called mixed research, which leverages qualitative and quantitative data.
2. Is qualitative research better or quantitative?
There’s no good or bad here. The effectiveness of each research type may vary from one use case to another. Different factors affect the type of research you choose to go with to access valuable insights.
3. Which research is difficult to conduct, qualitative or quantitative?
The answer to this question may be subjective.
However, based on the intricacy of the information you collect, data handling, analysis, and interpretation, conducting qualitative research may be a bit tricky compared to quantitative research.
4. Is the use of questionnaires limited to quantitative research only?
No! You can conduct surveys and use questionnaires as data collection instruments for both qualitative and quantitative research. However, you generally ask open-ended questions when conducting qualitative research.
Final Words
Many things distinguish qualitative from quantitative data. Both data types answer different questions for you. One provides you with a descriptive outlook, whereas the other helps you carry out numeric assessments.
Both data types answer different questions for you and provide you with relevant insights to make informed decisions.
The way you gather and analyze the data types may be different. However, each type of data facilitates diverse use cases and helps you deduce valuable findings.
The mix of qualitative and quantitative enables you to perform a detailed customer experience analysis, preparing you to establish lasting relationships.
Author Bio
Syed Balkhi is the founder of WPBeginner, the largest free WordPress resource site. With over 10 years of experience, he’s the leading WordPress expert in the industry. You can learn more about Syed and his portfolio of companies by following him on his social media networks.



