A software company launches a subscription service, and sign-ups surge. But soon, revenue stalls. Their static pricing model misses chances to charge more when high demand drives away smaller customers who need lower prices.
That’s where dynamic pricing models step in. These models enable businesses to adjust prices in real-time based on changing market conditions, customer behavior, demand fluctuations, and even competitor actions.
In this blog, we'll explore how businesses can leverage adaptive and dynamic pricing models in 2025 to enhance profitability and stay ahead of the competition.
Shortcuts:
- 5 Ways to Boost Profitability with Pricing Models
- The Future of Pricing in 2025
- FAQ: Dynamic Pricing and Adaptive Pricing Models

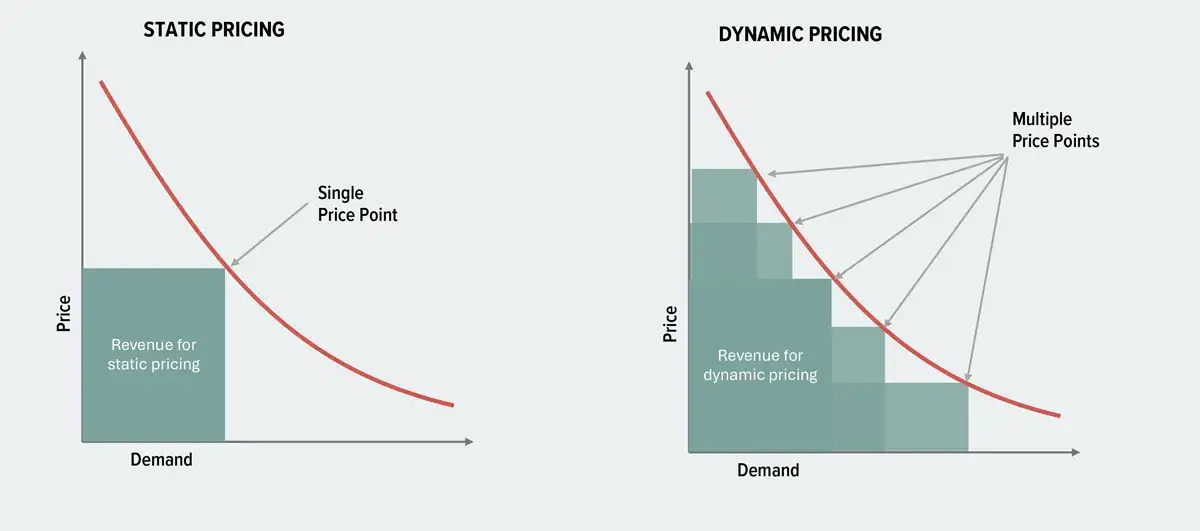
What is Dynamic Pricing?
Dynamic pricing is the practice of adjusting prices based on real-time data and market conditions.
Unlike traditional static pricing, which sets fixed prices, dynamic pricing offers flexibility and responsiveness to changes in demand, customer behavior, and competitor actions.
Here’s how it helps:
- Revenue optimization: Businesses can optimize revenue and sales volume by increasing prices when demand surges and offering discounts during slow periods.
- Improved customer segmentation: This pricing strategy enables companies to better segment their customer base, offering personalized prices to different groups based on their willingness to pay, behavior, or loyalty.
- Competitive advantage: Real-time price adjustments allow businesses to respond instantly to competitor price changes and market shifts, keeping margins intact.
- Inventory optimization: Adjusting prices based on inventory helps businesses optimize stock turnover. Overstocked items can be discounted to sell quickly, while in-demand, low-stock products can be priced higher.
5 Ways to Boost Profitability with Pricing Models
To maximize profitability in 2025, businesses should consider the following pricing strategies, each tailored to different industries and market needs:
1. Dynamic Pricing
Dynamic pricing is a flexible strategy in which prices fluctuate in response to real-time market demand, competition, consumer behavior, and inventory levels.
Ecommerce retailers, travel companies, and hospitality businesses widely adopt this approach.
For example, Amazon changes product prices multiple times a day based on competitor pricing, demand trends, and product availability. This approach helps Amazon stay competitive and maximize revenue.
To implement dynamic pricing models effectively:
- Invest in advanced analytics and pricing software that can quickly analyze vast amounts of data, providing insights into market trends and consumer behavior.
- If customers perceive pricing as unfair or manipulative, it can damage brand trust. Therefore, transparent pricing strategies that explain price fluctuations can help mitigate adverse reactions.
- Regularly review your pricing algorithms and strategies to ensure they align with changing market conditions and consumer preferences.
2. Segment-Based Pricing
Unlike dynamic pricing models, segment-based pricing adjusts prices for customer segments based on demographics, buying habits, location, and past interactions. This allows companies to optimize revenue potential.
Netflix is a clear example of this pricing model, offering various pricing tiers based on region and user preferences.
In some countries, Netflix provides lower subscription rates to capture a larger audience, while in wealthier areas, it charges more for premium content and features.
This strategy increases overall revenue and helps Netflix retain a diverse customer base by accommodating different willingness to pay. Here’s how to leverage this model successfully:
- Invest in robust data analytics tools to gather and analyze customer information effectively.
- Maintain a balance between pricing and perceived value. It’s essential to ensure that customers feel they are receiving value for their money, as this fosters loyalty and reduces churn.
- Be transparent about their pricing structures, clearly communicating the reasons behind price differences. This transparency helps build trust and minimizes any negative perceptions among customer
3. Time-Based Pricing
Time-based pricing involves varying prices according to the time of day, week, or season.
This strategy is particularly effective in industries such as transportation, entertainment, and utilities, where demand can fluctuate significantly due to external factors.
A prime example of time-based pricing can be found in ride-sharing apps like Uber.
During peak hours—such as rush hour or major events—Uber employs surge pricing, increasing rates to manage demand and incentivize more drivers to get on the road.
Conversely, during off-peak hours, the rates drop to encourage ride requests. For better results, businesses should:
- Analyze historical data to identify patterns in demand and pricing sensitivity. Understanding when customers are most likely to use their services allows for strategic price adjustments.
- Inform customers about the reasons behind price fluctuations. Transparency helps build trust and reduces the likelihood of negative perceptions.
- Monitor and refine their pricing strategies based on real-time data and market trends.
4. Geographic Pricing
Geographic pricing involves adjusting prices based on the customer's location.
This strategy is valuable for global e-commerce and localized service providers, enabling them to consider regional economic conditions, purchasing power, and market demand.
For example, McDonald's often adjusts its menu prices based on the local market.
In high-income areas, it may charge more for its offerings, while in developing regions, it implements lower prices to attract more customers. Similarly, here’s how coffee prices fluctuate in different countries:
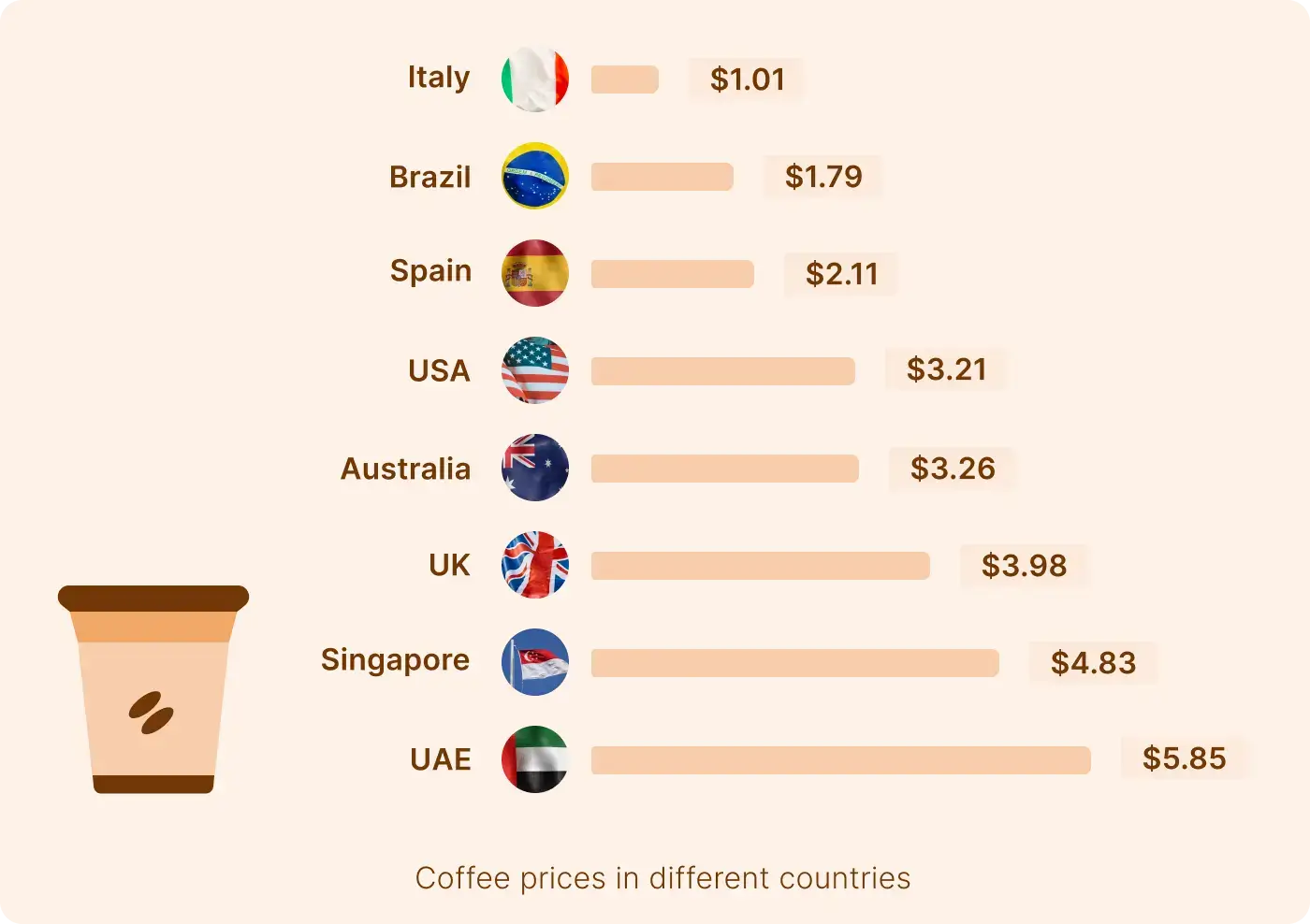
This model caters to each location's economic realities, helping to maintain a competitive advantage and drive sales across diverse markets. To implement geographic pricing effectively:
- Conduct thorough market research to understand different regions' economic conditions and price sensitivity. This includes analyzing local competition and consumer behavior.
- Consider the potential impact on brand perception. While adjusting prices can optimize revenue, it’s crucial to maintain a consistent brand image across regions.
- Employ technology and data analytics tools to monitor performance and adjust as needed.
5. Freemium to Premium Upsell
The freemium pricing model involves offering a free or low-cost product with the option for customers to unlock premium features at a higher price.
Businesses can attract a larger audience and create initial engagement by providing a free product version. Customers can experience the basic functionality without any financial commitment, which helps build brand loyalty and trust.
For instance, many SaaS platforms, such as Dropbox or Slack, offer free tiers that allow users to utilize core functionalities.
However, users must upgrade to a paid plan to access advanced features like increased storage, enhanced collaboration tools, or priority customer support. Here’s an excellent example by Spotify:
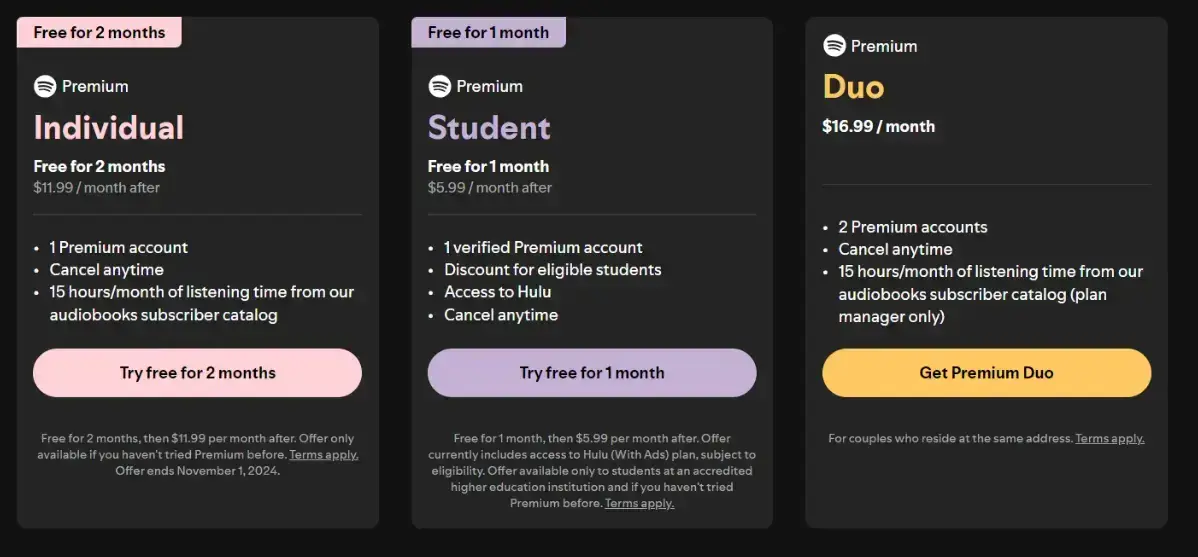
Here’s how to use it properly:
- Clearly define the value proposition of both the free and premium versions. Users should see the benefits of upgrading and understand what they’re missing in the free version.
- Focus on delivering an exceptional user experience in the free tier, as this can significantly influence the likelihood of conversion to paid plans.
- Remind users regularly of the premium features and provide incentives, such as limited-time discounts or trials, to encourage upgrades.
The Future of Pricing in 2025 and Beyond
Implementing dynamic pricing models is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity. As markets become more fluid and consumers seek personalized experiences, businesses must evolve their pricing strategies to maximize profitability.
However, implementing this pricing strategy requires care to avoid alienating customers or damaging the brand's reputation.
Understand your customers and communicate price changes transparently. When necessary, provide clear reasoning for fluctuations. Monitor your pricing system regularly to prevent sudden price hikes that could lead to a backlash.
Implementing A/B testing can help compare the effectiveness of different pricing strategies. Additionally, ensure your pricing tools are integrated with competitor monitoring platforms to stay ahead of the market.
These flexible pricing models allow businesses to position themselves for long-term success in an increasingly competitive global market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What technology tools can assist with adaptive pricing implementation?
Price optimization software utilizes algorithms and machine learning to analyze real-time data trends, customer behavior, and market conditions. Competitor monitoring tools help businesses stay informed about price changes in their market, enabling quicker reactions to competitor strategies.
Customer relationship management (CRM) systems also provide insights into customer purchasing behavior, preferences, and demographics.
2. How can businesses measure the success of their adaptive pricing strategies?
Businesses can monitor conversion rates from free to paid plans in freemium models, gather customer feedback on pricing changes, and analyze sales during peak and off-peak times. This gives them valuable insights to refine pricing strategies that align with market demands and consumer expectations.
3. How can businesses ensure customer trust while using adaptive pricing?
Communicate the reasons behind price changes and offer explanations for fluctuations, especially during promotions or dynamic pricing adjustments. Additionally, maintain consistent pricing practices and avoid sudden, unexplained price hikes to build and preserve trust.


